Powell says the stock market valuation is too high, how should option protection be played?
In his first public speech after the Fed announced a rate cut last week, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell continued to leave room for further rate cuts as he did at last week's press conference, hinting at cautious rate cuts in a challenging risk environment. During the question-and-answer session, Powell warned that the stock market valuation was too high, triggering a decline in the U.S. stock market.
In his speech on Tuesday, 23rd Eastern Time, Powell once again warned that the Fed's dual missions-full employment and price stability are both threatened, and the risks on both sides mean that there is no risk-free policy path. If interest rate cuts are too large or too fast, it may not be able to limit the control of high inflation and keep inflation above the Fed's 2% target. If monetary tightening is maintained for too long, it may unnecessarily drag down the labor market.
"There are upside risks to inflation and downside risks to employment in the short term-this is a challenging situation," Powell noted. Under the situation of "insufficient vitality and slightly weak labor market", the risk of employment downside has increased. It was because of the change in the balance of risks caused by increased employment risks that the Federal Reserve decided to cut interest rates last week.
Regarding tariffs, Powell reiterated that it is reasonable to expect that tariffs will have a short-lived impact on inflation and will only lead to one-time price fluctuations. However, a "one-time" fluctuation does not mean "immediate" and may last for several quarters. Powell still believes that the Fed must pay close attention to the possible lasting impact of tariffs, saying it must ensure that tariffs do not turn into persistent inflation problems.
Powell did not disclose any information in this speech, suggesting whether he would support interest rate cuts at the next Federal Reserve monetary policy meeting in October.
David Russell, global head of market strategy at TradeStation, commented that Powell is paving the way for the expectation that tariffs will lead to higher inflation in the fourth quarter of this year. He did so to give himself leeway in dealing with political pressure from the Trump administration, while tempering public opinion by emphasizing that the impact of tariffs is temporary. He said:
"Powell doesn't want to offend the White House, but he won't give in either. He leaves room to deal with possible inflationary pressures in the future. Powell doesn't intend to take a hawkish stance, but he is trying to avoid some strong demands for aggressive rate cuts."
Three major stock indexes refresh daily lows after Powell calls stock valuations'pretty high '
During the question-and-answer session after Tuesday's speech, Powell said that the U.S. labor market can no longer be considered solid, and now we do see substantial weakness in the labor market. Risks to financial stability have not increased. The banking sector has a good capital position and households are in good financial shape. Current financial stability risks are not high.
Regarding tariffs, Powell said that tariffs are not an important inflationary factor. The transmission mechanism of tariffs is not as significant as imagined. Most forecasts show that the transmission of tariffs will continue until 2026.
Powell believes that some asset prices are on the high side relative to historical levels. By many indicators, the stock market valuation is quite high.
Asked how attentive Fed officials are to market prices and whether they are more tolerant of higher price levels, Powell said:
"We will look at the overall financial situation and think about whether our policies are affecting the financial markets in the direction we expect. But you are right. From many indicators, such as stock prices, the current valuation is quite high."
Powell believes that companies hesitate because they don't know what to do. The U.S. economy is in a state of low layoffs and low hiring activity. Low unemployment and a low-employment economy are tough for young workers.
When it comes to artificial intelligence (AI), Powell believes it is too early to judge the impact of AI. AI means that certain positions will be eliminated. Research shows that AI is not a major reason for the slowdown in hiring. The hiring slowdown is partly related to the uncertainty of government public policies.
Powell also said that the Fed's monetary decisions will not consider partisan politics. Many people don't believe this. Powell criticized those who argued that some of the Fed's moves were politically motivated, calling their claims "baseless."
After Powell mentioned that the stock market was overvalued, the Dow turned down. As a result, all three major U.S. stock indexes turned down intraday, and the S&P and Nasdaq expanded their losses. Shortly after Powell's speech, the three major indexes set new daily lows. The Nasdaq fell nearly 1.1%, the S&P fell more than 0.7%, and the Dow fell slightly more than 100 points or more than 0.2%.
What exactly is the collar strategy?
To protect the downside risk of stocks, there is a strategy of buying put options (Protective Put), and to reduce the cost of holding stocks, you can sell Covered Call options (Covered Call). In order to give consideration to both, Collar-this new strategy was born.
The operation method of collar option is to buy an out-of-the-money put option as insurance on the premise of holding stocks, and at the same time sell an out-of-the-money call option to pay the cost of insurance. This is equivalent to putting a Collar on the stock, and the income of the stock is locked in it, hence the name of the Collar option. The collar option is in fact a combination of Protective Put and Covered Call, which limits the risk of downside at the expense of removing some of the possibility of upside profit.
Collar options are available when traders have a bullish position in the underlying market and want to protect the position from market downside shocks. When the full cost of a put option is covered by selling a call option, it is called a zero-cost collar strategy.
Nvidia Collar Options Strategy Case
Let's say an investor owns 100 shares currently at $178.43$Nvidia (NVDA) $, investors are not sure how prices will change in the near future and want to buy an insurance policy for their positions. You can use the collar strategy.
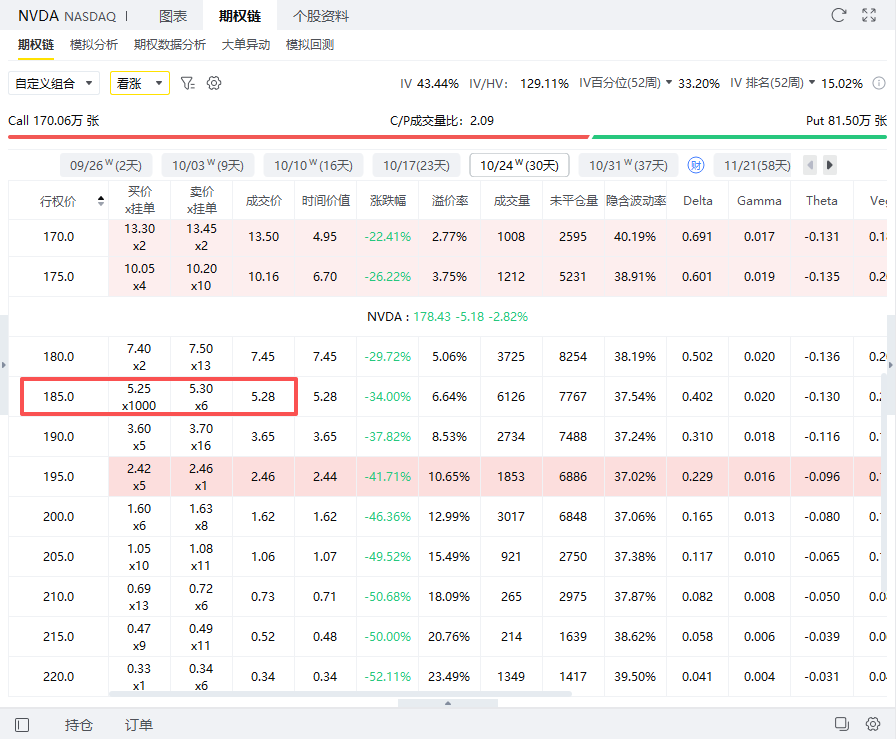
In the first step, investors can sell a call option with an exercise price of $185 and an expiration date of October 24 at a price of $528, earning $528.
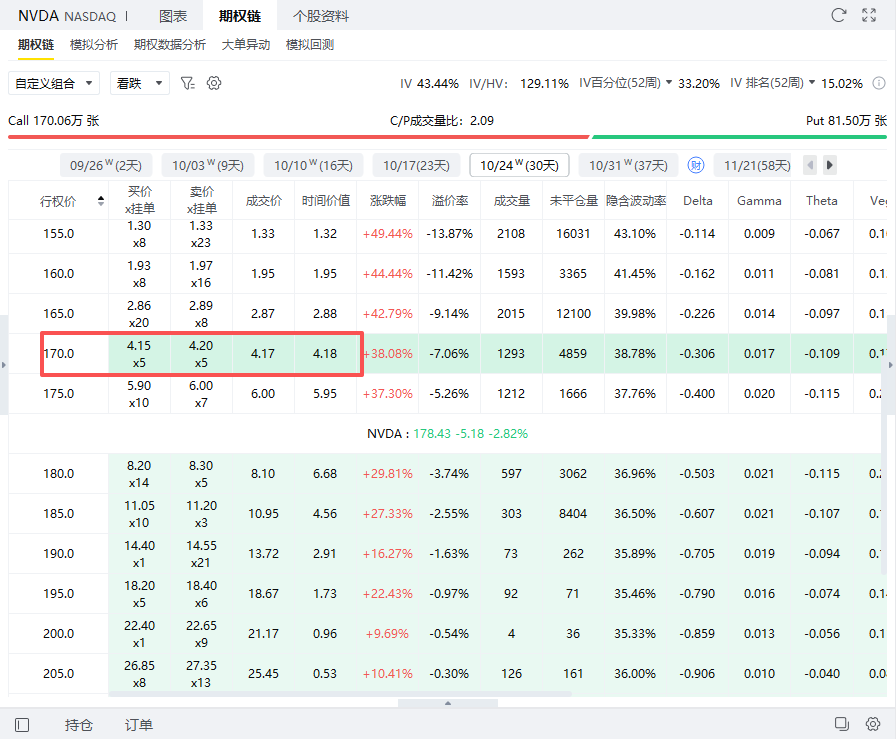
In the second step, you can also buy a put option with an exercise price of $170 and an expiration date of October 24 at a price of $4.17 (costing $417).
This strategy can play a protective role when Nvidia's stock price falls sharply, while earning premium income by selling call options and reducing the cost of buying insurance.
Operational logicInvestors own 100 shares of Nvidia (now $178.43).
Sold a call option with an exercise price of $185 and an expiration on October 24, earning $528.
It costs $417 to buy a put option with an exercise price of $170 and an expiration on October 24. Net premium revenue was $111.
Maximum benefitIf Nvidia's stock price is higher than or equal to $185 at expiration, the stock's floating profit will be locked in by the call option cap.
The stock went from 178.43 to 185, making a profit of $657.
Sold call loss (185 + partial abandonment), but still retain $528 income.
The buy put option expires and becomes invalid.
Total revenue = 657 + 111 =$768。
Maximum lossIf Nvidia falls to $170 or less at expiration:
Stock loss = (170-178.43) × 100 =-$843.
The profit from buying the put option offsets this loss.
Selling the call option retains $528 in income.
Net result =-843 + 528 + (put option profit filled to 170 floor price) ≈+111 USD。 The maximum loss is therefore limited toWon't be less than $111 in net income。
Break-even pointAround the stock price of 178.43:
If the stock price remains unmoved and the investor's existing stock is neither rising nor falling, the net income of the option part is $111.
The actual break-even point is about 178.43 (cost of position)-1.11 (net income per share) =$177.32。
Disclaimer: Investing carries risk. This is not financial advice. The above content should not be regarded as an offer, recommendation, or solicitation on acquiring or disposing of any financial products, any associated discussions, comments, or posts by author or other users should not be considered as such either. It is solely for general information purpose only, which does not consider your own investment objectives, financial situations or needs. TTM assumes no responsibility or warranty for the accuracy and completeness of the information, investors should do their own research and may seek professional advice before investing.