$Nike (NKE) $The latest quarterly financial report will be released on December 18, 2025 (after the U.S. stock market closes). The market is paying attention to the profit inflection point brought about by inventory destocking and product mix adjustment and the marginal improvement of channel relationship repair.
The market consensus expects Nike's total revenue this quarter to be US $12.221 billion, a year-on-year increase of 0.77%; Gross margin forecast is not disclosed; Net profit or net profit margin forecast is not disclosed; Adjusted earnings per share are expected to be $0.38, down 40.64% year over year, respectively; EBIT is expected to be $696 million, a year-over-year decrease of 37.46%. Among the main businesses disclosed by the company last quarter, Nike brand revenue was US $11.362 billion, Converse revenue was US $366 million, and the company's main adjustment item was-US $80 million. At present, the company's main business highlights are the high proportion of Nike brand and the promotion of product line restructuring of professional sports shoes and clothing; The highlight of the existing business with the greatest development prospects is the channel repair and new product drive of the Nike brand. The revenue of the Nike brand is US $11.362 billion, and the year-on-year information has not been disclosed.
Nike's revenue last quarter was US $11.720 billion, a year-on-year increase of 1.13%; The gross profit margin was 42.18%, and the year-on-year information was not disclosed; The net profit attributable to the parent company was US $727 million, the net profit rate was 6.20%, and the year-on-year growth rate was 244.55% (month-on-month indicator); Adjusted earnings per share were $0.49, down 30.00% year-over-year. Last quarter, the company's business focused on inventory destocking and product mix optimization, and the expense and discount strategy were coordinated to improve channel quality. In terms of business, Nike brand revenue was US $11.362 billion, Converse revenue was US $366 million, and the company's main adjustment item was-US $80 million. The Nike brand contributed the highest but the year-on-year information was not disclosed.
Recently, many institutions have raised Nike's target price and profit expectations after the last quarter's financial report, and bullish views are dominant. Morgan Stanley said that "Nike's fundamentals are likely to bottom out", raised the target price from $61.00 to $64.00, and maintained a rating that keeps pace with the market; Citigroup pointed out that "sales in the final fiscal quarter exceeded expectations" and raised its target price to $68.00; UBS said that "the trend turned faster than expected, inventories improved, and the sales outlook was better than expected", and the target price was raised to $63.00.
Combined with Reuters's statistics on financial report prospects, the total proportion of "buy/strong buy" in the analyst rating structure is relatively high, and the market has confidence in the sustainability of inventory management and new product drive. On the whole, the proportion of bullish views is higher. The core reasons are that the actual values of revenue and profit in the previous quarter are better than consensus expectations, the visibility of improved channel and inventory indicators has increased, and the mid-term positive impact of product mix restructuring on gross profit margins; The short-term profit pressure is within expectations, but the marginal improvement signal is clear. If the revenue achieves a slight increase in this quarter and the cost pressure is controllable, the institution expects that the subsequent profit will gradually recover.
Reverse Calendar Spread Reverse Calendar Spread
A reverse calendar spread is aSell near-month options, buy far-month optionsStrategy, the strike price of options is usually the same.
As opposed to "positive Calendar Spread (Calendar Spread: buy near month, sell far month)".
When to Use Reverse Calendar Spreads?
Usually used to judge:
Expect short-term volatility to decline
Because you sell in the near month (θ is fast, vega sensitivity is high), if the short-term IV falls → the seller makes more money.
It is expected that the underlying price will experience a large breakout in the short term
The reverse calendar maximum gain point usually occurs at a deviation from the strike price, rather than near it.
You wish:
Near-month optionsQuick zeroing or limited loss
Far Month OptionsBenefit from greater absolute price volatility
Hence it isSee the direction fluctuates sharplyOrLook at short-term IV declineStrategy.
1. Strategy construction
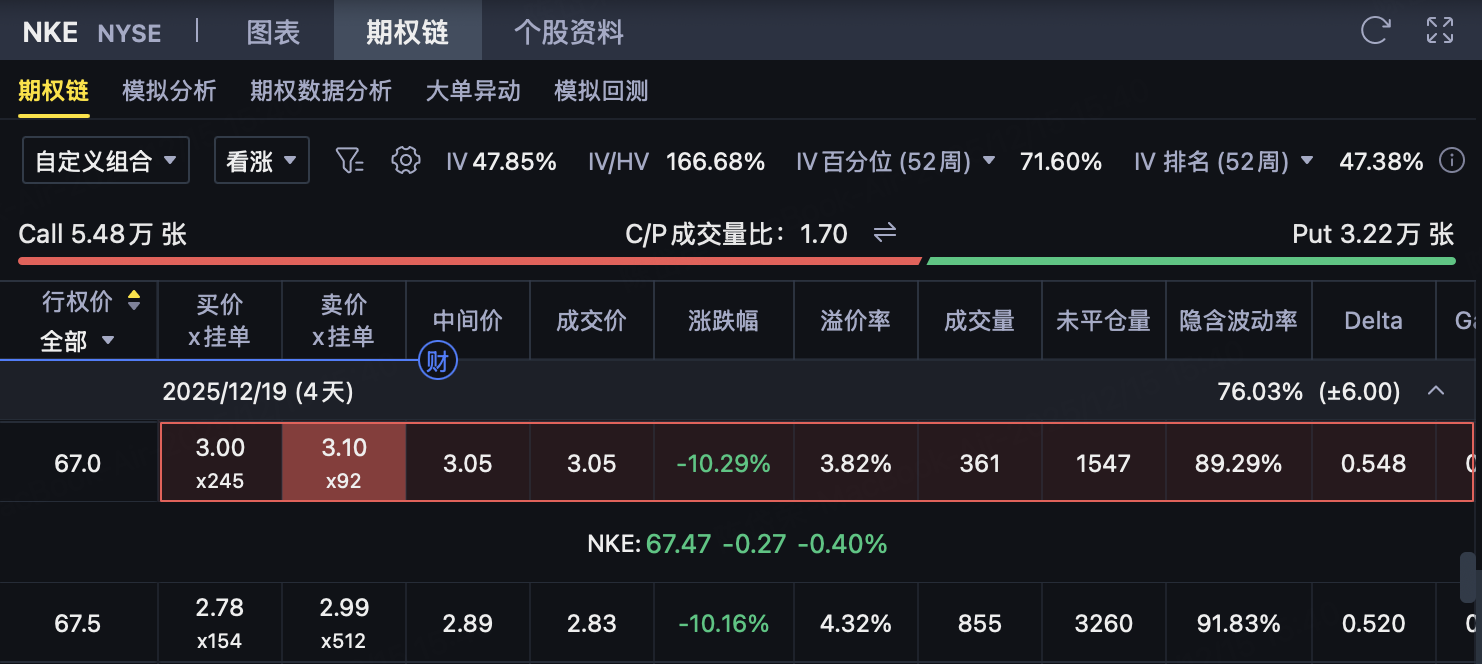
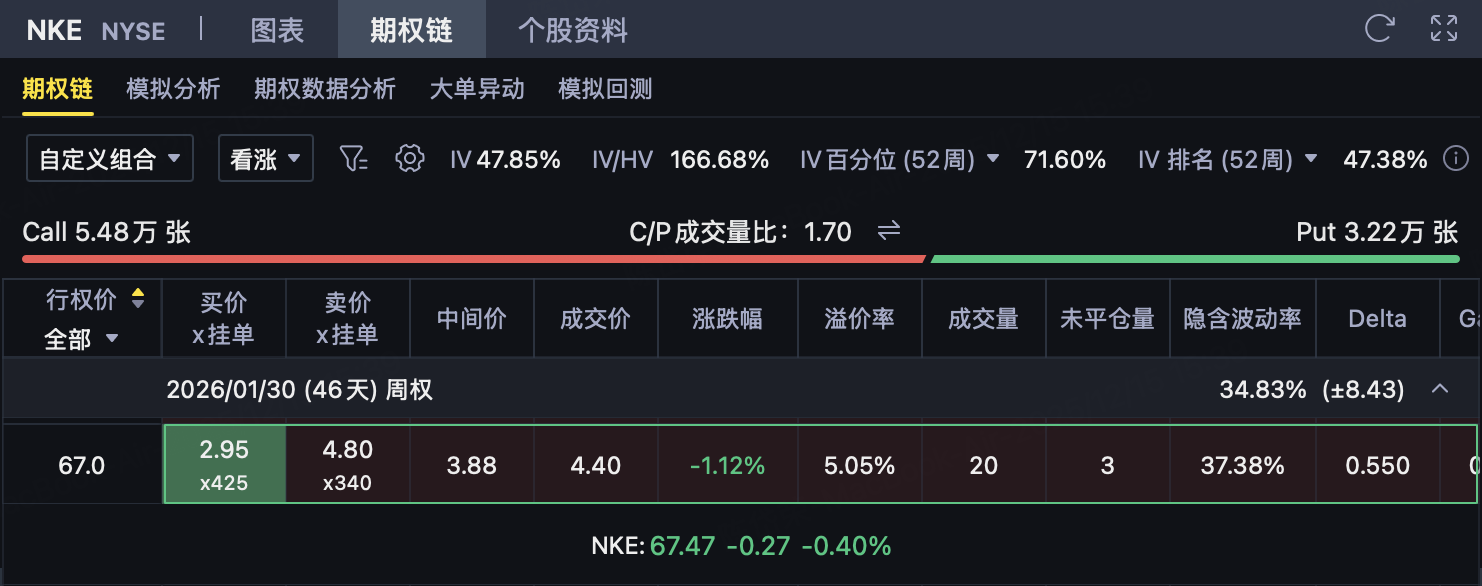
As Nike (NKE) is about to announce its financial report after the U.S. stock market closes on December 18, the pricing of short-term options includes a large number ofEvent Premium。
In this context, investors adopt:
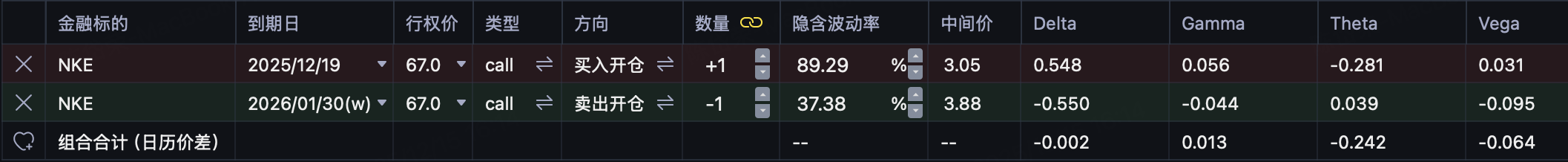
Buy 67 Call on 2025/12/19
Sell 67 Call of 2026/01/30
The combination is established as:
Net premium (combined price is-1.35)
Therefore, the core expectation of this strategy is not "price skyrocketing", but:
After the financial report incident landed, the short-term premium declined rapidly.And this decay rate is faster than the value change of forward options.
The Greeks of this combination are as follows:
What investors want to see:
Front-month option values collapse rapidly
Far-month options do not appreciate in equal proportion
So that that combination priceFurther drop
2. Profit and loss driving logic
Time Factor: The Rapid Disappearance of Short-term premium
Reverse calendarThe first principle is the time structure:
Front-month options bought:
Very short time remaining
After EarningsTheta amplifies dramatically
Far-month options sold:
Time value thick
Single day Theta is smaller
So, as long as:
Stock price after earningsThere is no sharp trend market
Front-month options converge rapidly towards 0
👉The combination price will naturally go lower (favorable)
Stock price path: avoid "big and fast unilateral market"
Exactly the opposite of a forward calendar:
Reverse Calendars Don't Like Big, Fast Moves
Especially dislike:
The stock price rose rapidly and stood firm after the earnings report
Or kill quickly and continue to expand
The reason is that:
Positive Gamma will raise the market value of the portfolio amid large volatility
Thereby causingCombination price recovery → unfavorable
Therefore, the reverse calendar prefers:
Price reacts quickly after earnings, but then blunts
Or quickly return to the vicinity of the strike price after short-term fluctuations
Implied Volatility: IV Pullback
In the reverse calendar:
Combination Vega is negative
IV DownIs advantageous
4. Main risks of reverse calendar spreads
< h3 id = "id _1044353213 "> Persistent unilateral market after financial report (maximum risk)
Stock Quickly Breaks 67 and Continues
Or fall sharply below and form a trend
Can result in:
The intrinsic + time value of Far Moon Call expands rapidly
Portfolio price is inflated → loss
Long-term implied volatility is repriced
Earnings reveal structural issues
Market upgrades medium-and long-term
This directly hurts:
Sold 1/30 Call
Make the combination price rebound
Short-term "excessive volatility" after financial report
Even if it ultimately goes back to 67
But there is a violent jump in that path
It may also be:
Trigger the Gamma effect
Amplify portfolio market capitalization in the short term (unfavorable)
5. A summary that really belongs to the reverse calendar
The reverse calendar is not a bet on "moving more",Instead, bet that "after moving, the near month will die faster than the far month".
The essence of your deal is:
With a limited initial cost
Go Bet:
Earnings don't trigger long-term trends
Market uncertainty over NKE is mostly'short-term '
Comments