U.S. Economy Facing Rising Risks of Recession
Since January, recession risks in the U.S. economy have become increasingly salient. Optimistic market sentiment has subsided, and policy shifts under the Trump administration—including tariff hikes, federal budget cuts, and layoffs at Doge Corporation—have significantly dampened economic momentum.
Key indicators show evident deterioration:
On March 11, the U.S. 10-year treasury yield fell to 4.28%, down from January's optimistic peak of 4.79%. The U.S. Dollar Index also sharply declined from 110.17 (January 13) to 103.39 (March 11).
The Atlanta Fed drastically cut its Q1 2025 GDP growth forecast from 3.9% to -2.4%, citing weak consumer spending and net exports.
Recent retail sales figures notably missed expectations, consumption growth slowed sharply, and credit card delinquency rates reached their highest since 2012.
Manufacturing investment weakened as the ISM PMI new orders index plunged 6.5 percentage points in February.
Importantly, the Trump administration deliberately aims to slow down economic activity to relieve the unsustainable debt burden. U.S. national debt surpassed $36 trillion by late 2024, with projected interest payments between $1.2 and $1.3 trillion in 2025 under current rates. Treasury Secretary Bessent publicly acknowledged the strategy to induce a short-term recession (within 6-12 months) through tariffs and spending cuts, forcing the Fed to lower interest rates and thus alleviate the debt crisis.
Positive Chinese Policies Accelerating Economic Recovery
By comparison, China's economic policies are much more proactive. Recent government announcements explicitly promise timely cuts to reserve requirement ratios (RRR) and interest rates, demonstrating determination to ensure stable growth.
Local government debt-control adjustments further support economic stability by easing restrictive deleveraging pressures on investment and infrastructure mainly at the local level.
Recent macroeconomic data reflect China's accelerated recovery:
The February manufacturing PMI rebounded 1.1 points month-on-month to 50.2%, returning to expansion territory.
Financing demands in the real economy surged significantly, with total social financing hitting a record high of 7.1 trillion RMB in January 2025, up substantially year-on-year, driven by higher RMB loans and government bond issuance.
The government continues to emphasize domestic-demand-led strategies, alongside structural reforms to unlock consumption, enhance productivity, and boost manufacturing competitiveness. Although U.S. tariffs might briefly impact exports, structural upgrades and accelerated import substitution trends ensure reliable support for external trade recovery.
Narrowing China-U.S. Interest Rate Differential Driving Capital Inflows
Due to diverging economic paths, China-U.S. sovereign yield spreads have narrowed considerably. By March 11, the yield gap between Chinese and U.S. bonds declined from 3.1504 percentage points on January 13 to 2.4116 percentage points.
This narrowing spread has accelerated international capital inflows into China. Furthermore, China's trade surplus reached $170.51 billion in January-February, significantly higher than $124.64 billion in the same period last year. Additionally, increased northbound investment inflows expanded the capital account surplus, strengthening the RMB's appreciation prospects.
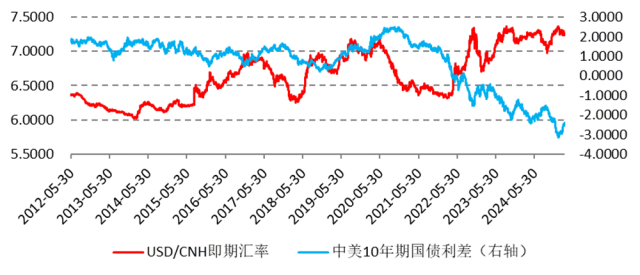
Conclusion: RMB Set for Further Appreciation Against USD
In summary, the growth outlook between China and the U.S. has reversed significantly:
The U.S. economy faces rising recession risks caused by intentional policy actions and market conditions, resulting in declining dollar strength and Treasury yields.
China, benefiting from proactive fiscal and monetary policies and recovery in manufacturing and investments, demonstrates strong momentum and a stable growth outlook.
The narrowing interest rate spread drives substantial international capital inflows to China, coupled with robust trade surplus growth and steady foreign capital increases, collectively enhancing the RMB's appreciation momentum.
$E-mini Nasdaq 100 - main 2503(NQmain)$ $E-mini Dow Jones - main 2503(YMmain)$ $E-mini S&P 500 - main 2503(ESmain)$ $WTI Crude Oil - main 2504(CLmain)$ $Gold - main 2504(GCmain)$
Comments